
Semiconductor nanomaterials
Semiconductor nanomaterials
Semiconductor nanomaterials
Semiconductor nanomaterials
The synthesis of new nanoscale materials with unique physical properties can enable revolutionary advances in science and technology. The Lee group are leaders in the design, synthesis, characterization, and hierarchical assembly of nanoscale materials. In addition, the Lieber group are leaders in characterizing fundamental structural and physical properties of these materials, and also fabricating and characterizing novel device structures and arrays of devices that are used in studies at the interface with biology and medicine. Research areas being pursued include the following:
-
Nanomaterials synthesis. We are pursuing studies of the growth and characterization of nanomaterials with an emphasis on the design and synthesis of nanowires with novel morphologies and complex modulation of dopant and/or composition in order to realize building blocks with novel electronic/photonic properties and/or morphologies that enable new opportunities in the life sciences.
-
Nanomaterials properties. Illuminating fundamental structural and physical properties of newly synthesized nanomaterials is central to both further synthetic advances and ‘applications’ of the nanostructures in other areas. In this regard, the Lieber group carries out state-of-the-art electron microscopy work to characterize atomic-level and up structure and composition, as well as measurements at the single nanostructure level to reveal electrical and optical properties.
-
Assembly of nanostructures. Controlled assembly of nanoscale wires and other nanomaterials is central to realizing our bottom-up paradigm of nanodevice arrays through functional systems, and as such we have maintained strong effort in developing both sophisticated and practical methods for hierarchical organization of nanomaterials. These studies are often motivated by and demonstrated with the development of novel tools and technologies that can open up opportunities at the interface with other areas of science.
The synthesis of new nanoscale materials with unique physical properties can enable revolutionary advances in science and technology. The Lee group are leaders in the design, synthesis, characterization, and hierarchical assembly of nanoscale materials. In addition, the Lieber group are leaders in characterizing fundamental structural and physical properties of these materials, and also fabricating and characterizing novel device structures and arrays of devices that are used in studies at the interface with biology and medicine. Research areas being pursued include the following:
-
Nanomaterials synthesis. We are pursuing studies of the growth and characterization of nanomaterials with an emphasis on the design and synthesis of nanowires with novel morphologies and complex modulation of dopant and/or composition in order to realize building blocks with novel electronic/photonic properties and/or morphologies that enable new opportunities in the life sciences.
-
Nanomaterials properties. Illuminating fundamental structural and physical properties of newly synthesized nanomaterials is central to both further synthetic advances and ‘applications’ of the nanostructures in other areas. In this regard, the Lieber group carries out state-of-the-art electron microscopy work to characterize atomic-level and up structure and composition, as well as measurements at the single nanostructure level to reveal electrical and optical properties.
-
Assembly of nanostructures. Controlled assembly of nanoscale wires and other nanomaterials is central to realizing our bottom-up paradigm of nanodevice arrays through functional systems, and as such we have maintained strong effort in developing both sophisticated and practical methods for hierarchical organization of nanomaterials. These studies are often motivated by and demonstrated with the development of novel tools and technologies that can open up opportunities at the interface with other areas of science.
The synthesis of new nanoscale materials with unique physical properties can enable revolutionary advances in science and technology. The Lee group are leaders in the design, synthesis, characterization, and hierarchical assembly of nanoscale materials. In addition, the Lieber group are leaders in characterizing fundamental structural and physical properties of these materials, and also fabricating and characterizing novel device structures and arrays of devices that are used in studies at the interface with biology and medicine. Research areas being pursued include the following:
-
Nanomaterials synthesis. We are pursuing studies of the growth and characterization of nanomaterials with an emphasis on the design and synthesis of nanowires with novel morphologies and complex modulation of dopant and/or composition in order to realize building blocks with novel electronic/photonic properties and/or morphologies that enable new opportunities in the life sciences.
-
Nanomaterials properties. Illuminating fundamental structural and physical properties of newly synthesized nanomaterials is central to both further synthetic advances and ‘applications’ of the nanostructures in other areas. In this regard, the Lieber group carries out state-of-the-art electron microscopy work to characterize atomic-level and up structure and composition, as well as measurements at the single nanostructure level to reveal electrical and optical properties.
-
Assembly of nanostructures. Controlled assembly of nanoscale wires and other nanomaterials is central to realizing our bottom-up paradigm of nanodevice arrays through functional systems, and as such we have maintained strong effort in developing both sophisticated and practical methods for hierarchical organization of nanomaterials. These studies are often motivated by and demonstrated with the development of novel tools and technologies that can open up opportunities at the interface with other areas of science.
The synthesis of new nanoscale materials with unique physical properties can enable revolutionary advances in science and technology. The Lee group are leaders in the design, synthesis, characterization, and hierarchical assembly of nanoscale materials. In addition, the Lieber group are leaders in characterizing fundamental structural and physical properties of these materials, and also fabricating and characterizing novel device structures and arrays of devices that are used in studies at the interface with biology and medicine. Research areas being pursued include the following:
-
Nanomaterials synthesis. We are pursuing studies of the growth and characterization of nanomaterials with an emphasis on the design and synthesis of nanowires with novel morphologies and complex modulation of dopant and/or composition in order to realize building blocks with novel electronic/photonic properties and/or morphologies that enable new opportunities in the life sciences.
-
Nanomaterials properties. Illuminating fundamental structural and physical properties of newly synthesized nanomaterials is central to both further synthetic advances and ‘applications’ of the nanostructures in other areas. In this regard, the Lieber group carries out state-of-the-art electron microscopy work to characterize atomic-level and up structure and composition, as well as measurements at the single nanostructure level to reveal electrical and optical properties.
-
Assembly of nanostructures. Controlled assembly of nanoscale wires and other nanomaterials is central to realizing our bottom-up paradigm of nanodevice arrays through functional systems, and as such we have maintained strong effort in developing both sophisticated and practical methods for hierarchical organization of nanomaterials. These studies are often motivated by and demonstrated with the development of novel tools and technologies that can open up opportunities at the interface with other areas of science.
The synthesis of new nanoscale materials with unique physical properties can enable revolutionary advances in science and technology. The Lee group are leaders in the design, synthesis, characterization, and hierarchical assembly of nanoscale materials. In addition, the Lieber group are leaders in characterizing fundamental structural and physical properties of these materials, and also fabricating and characterizing novel device structures and arrays of devices that are used in studies at the interface with biology and medicine. Research areas being pursued include the following:
-
Nanomaterials synthesis. We are pursuing studies of the growth and characterization of nanomaterials with an emphasis on the design and synthesis of nanowires with novel morphologies and complex modulation of dopant and/or composition in order to realize building blocks with novel electronic/photonic properties and/or morphologies that enable new opportunities in the life sciences.
-
Nanomaterials properties. Illuminating fundamental structural and physical properties of newly synthesized nanomaterials is central to both further synthetic advances and ‘applications’ of the nanostructures in other areas. In this regard, the Lieber group carries out state-of-the-art electron microscopy work to characterize atomic-level and up structure and composition, as well as measurements at the single nanostructure level to reveal electrical and optical properties.
-
Assembly of nanostructures. Controlled assembly of nanoscale wires and other nanomaterials is central to realizing our bottom-up paradigm of nanodevice arrays through functional systems, and as such we have maintained strong effort in developing both sophisticated and practical methods for hierarchical organization of nanomaterials. These studies are often motivated by and demonstrated with the development of novel tools and technologies that can open up opportunities at the interface with other areas of science.
Functional nanocomposites
Low-dimensional carbon nanomaterials (e.g., carbon nanotube (CNT), graphene, and fullerene) based on threedimensional (3D) structures have recently attracted much attention as building blocks for water purification and biochemistry because of their high adsorption capacity, lightweight, extraordinary chemical and mechanical durability, and superior electrical and thermal conductivity. Among these materials, graphene, which consists of a one-atom thick crystal of sp2 carbon atoms in a two-dimensional (2D) honeycomb lattice, is advantageous due to its high adsorption capacity for specific organic compounds or biomaterials with aromatic structures resulting from the strong intermolecular interaction between the delocalized π-bonds. As a graphene derivative, graphene oxide (GO) has become an attractive material because it can be readily mass-produced via the chemical exfoliation of graphite powders. In addition, because of the abundant oxygen (O)- containing functional groups, this material can be easily dispersed in aqueous solutions and strongly interacts with a variety of organic and bioi-materials via hydrogen bonding and ionic interactions.
-
Design and synthesis of functional nanomaterials: studies of fabrication of 3D nanocomposites with high surface area and control their functionality.
-
Application of functional nanomaterials: studies on the correlation between structural properties and chemical interaction between organic and bio-materials for environmental and biosensor applications.
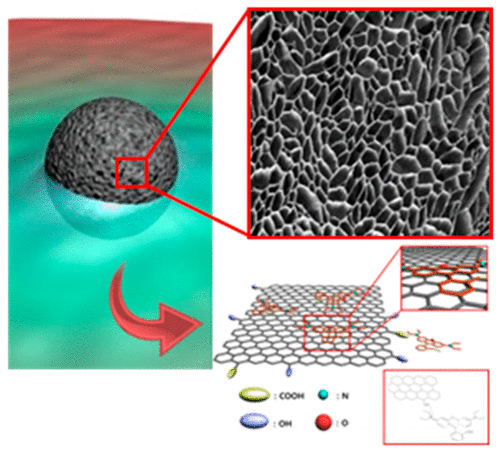 Graphene based composites for absorption of organic molecules |
|---|
 Absorption test of organic materials |
 Graphene composites |
 Porous composites |

